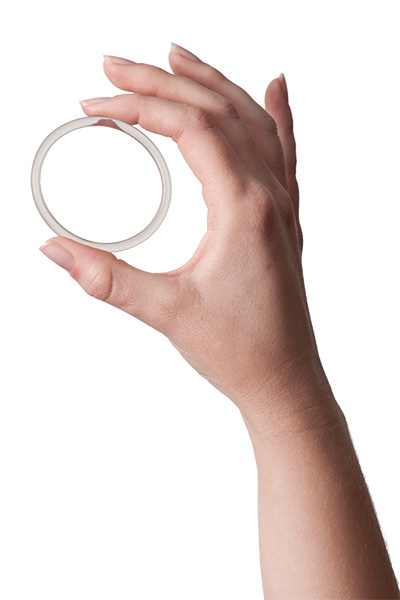
The vaginal ring is a soft plastic ring about 5cm in diameter. It contains two hormones (oestrogen and progestogen), similar to those in the combined oral contraceptive pill.
A ring is placed in the vagina and it stays there for three weeks. It is then removed for one week and during this ring-free week you have a monthly bleed (like a period). After the fourth week, you insert a new ring and begin the cycle again.
How does it work?
- Stops the ovaries from releasing an egg.
- Thickens the mucus at the entrance to the uterus (cervix) to stop sperm from moving into the uterus.
The vaginal ring works in a similar way to the combined contraceptive pill. The difference is the way the hormones in the ring are absorbed slowly through the walls of the vagina into the bloodstream.
How well does it work?
The vaginal ring is 99.7% effective at preventing pregnancy when used perfectly, but in real life it can be less effective (91%) if inserted late or used incorrectly.
What are the benefits?
- A good option if you have trouble remembering to take a pill every day.
- It does not need to be ‘fitted’ and the same size suits everyone.
- It is not affected by vomiting or diarrhoea because the hormones are absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
- Periods usually become lighter, more regular and less painful.
- Acne often improves.
- Symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), such as mood changes before a period, often improve or go completely.
What are the downsides?
- The vaginal ring does not protect against STIs but can be used at the same time as condoms.
- You must remember to remove the ring after three weeks and insert a new one a week later. Some people find it useful to set a reminder or alarm on their phone to help them remember.
- The ring is more expensive than some other forms of contraception.
- Some people don’t feel comfortable inserting the ring into their vagina.
Are there side effects?
Most people have very few side effects and those who do get them often find they settle down within the first few months. You may experience:
- tender breasts
- headaches
- feeling sick (nausea)
- bloating
- mood changes
It is rare to have serious health problems with the vaginal ring, especially if you are young. This includes a small risk of blood clots, called deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Can anyone use the ring?
You can’t use the vaginal ring if you have:
- a history of blood clots deep in the leg or lungs
- some health problems such as certain types of migraines, heart disease and severe liver conditions – talk to your doctor about any medical conditions you may have
Where do you get it?
The vaginal ring is available with a prescription from your doctor or Family Planning Australia clinic.